At the recent quarterly reporting conference, Intel CEO Lip-Bu Tan said that developing the company’s competencies in artificial intelligence will be a key factor in restoring its market position. Intel plans to move to an integrated approach, offering customers processors and ready-made server systems with software similar to Nvidia, which successfully monetizes its AI solutions.
Intel will be unable to fix the situation in this market segment quickly. It must audit its existing products to identify the most suitable AI systems and robotics for market development. Peripheral computing will also receive attention in Intel’s strategy. Nevertheless, skeptics believe there are limited opportunities for Intel to gain a foothold in the highly competitive market of artificial intelligence and automated trading.
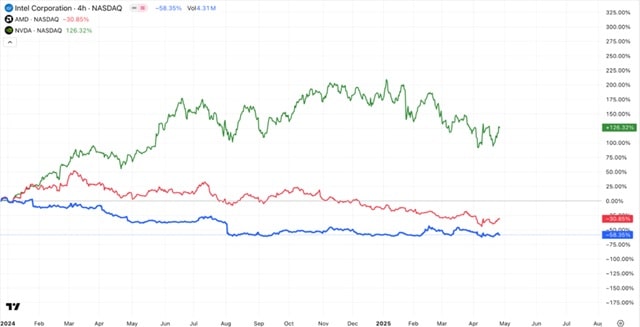
Despite the recent rebound in the company’s shares, Intel’s outlook seems less optimistic compared to AMD’s or Nvidia’s in the long run.
First, these areas are dominated by Nvidia, which won’t step back without a fight. Second, cloud market players like Amazon and Google are developing optimal computing components tailored to their own needs, and Amazon stock, for instance, reflects strong investor confidence in its technological advancements.
In the first quarter of 2024, Intel managed to keep revenue stable at $12.7 billion, matching the figure from the same period last year. This result exceeded analysts’ expectations, which had predicted $12.3 billion. However, investors were disappointed by the forecast for the second quarter: management expects lower revenues, leading to a 5% drop in the company’s share price.
Investors had anticipated a second-quarter revenue forecast of $12.82 billion, while the midpoint of the company’s projected range — from $11.2 billion to $12.4 billion — is $11.8 billion, falling short of market expectations. In addition, this level of revenue would represent a $1 billion year-on-year decline. Intel’s management explained that its forecast reflects macroeconomic instability.
Previously, Intel acquired startups specializing in computing accelerators, such as Habana Labs and Nervana Systems. However, this approach did not yield the expected results. Now the company intends to develop AI technologies using its internal resources. This means Intel is not planning any major acquisitions in the near future, instead focusing on internal development and integration of solutions.
Intel’s management has warned that the company will face several challenges in the second quarter:
- An increase in tariffs due to trade conflicts will reduce the overall market size and drive up prices.
- A more significant revenue decline in the server segment compared to the client segment.
- A drop in demand for contract manufacturing, as customers accelerated orders ahead of rising US duties, is expected to dampen activity.
Additionally, Intel’s profit margin in the second quarter is projected to fall to 36.5%, significantly lower than its historical level of 60%, raising even more concerns among investors. Intel’s net losses in the first quarter reached $800 million, double the losses recorded during the same period last year.
The company is ready to cut costs. Operating expenses are planned to be kept within $17 billion this year, down from the previous estimate of $17.5 billion, and capital expenditures are expected to be reduced from $20 billion to $18 billion. For next year, operating expenses are intended to be kept within $16 billion.
Intel’s strategic pivot toward AI is a logical step, but the company will have to prove it can compete with players like Nvidia and AMD without relying on acquisitions.
So far, the weak forecast and pressure from macroeconomic factors have left investors with cautious expectations. Will Intel be able to reverse the trend? The answer will become clearer in the next reporting period.